Distal Radius Fracture
What is a Distal Radius Fracture?
Distal radius fractures are very common in paediatrics (~25%) and older populations (~20%). This article will deal only with adult distal radius fractures. If you’d like to know more about paediatric distal radius fractures click here.
A distal radius fracture predominantly occurs through a fall onto an outstretched hand/wrist. The universal classification separates these fractures into extra-articular (not involving the joint), intra-articular (involving the joint) and displacement/non-displacement. Extra-articular fractures will be the focus of our article as intra-articular fractures require close examination for surgical considerations.
When you fall onto your wrist there is 78% axial load transferred to the distal end of the radius. This is why there is a greater chance of a fracture occuring in your radius. Depending on the position of your wrist when landing (flexed or extended)

will result in 2 more common types of distal radius fractures, the Colles and Smith’s ( sometimes called a reverse Colles) fractures. There are also other distal radial fractures in that of a Barton’s and Chauffer fracture.
Colles Fracture
A Colles fracture is a distal radius fracture that occurs when landing with your wrist in an extended position. It is common to have a degree of dorsal displacement with the fracture fragment. It is important to have this assessed with an Xray to determine the extent of displacement. There are some other complications resulting from this type of mechanism in that of injury to local soft tissue including tendons and nerves. Our Physiotherapists will conduct a thorough history and physical examination to determine the full extent of your injuries. The good news is that many distal radius fractures heal conservatively with appropriate splinting and rehabilitation.
Smith’s Fracture
A Smith’s (or reverse Colles) radius fracture occurs when landing with your wrist in a flexed position. It is common to have a degree of volar displacement with the fracture fragment. It is important to have this assessed with an Xray to determine the extent of displacement. There are some other complications resulting from this type of mechanism in that of injury to local soft tissue including tendons and nerves. Our Physiotherapists will conduct a thorough history and physical examination to determine the full extent of your injuries. The good news is that many distal radius fractures heal conservatively with appropriate splinting and rehabilitation.
Treatment for a Distal Radius Fracture
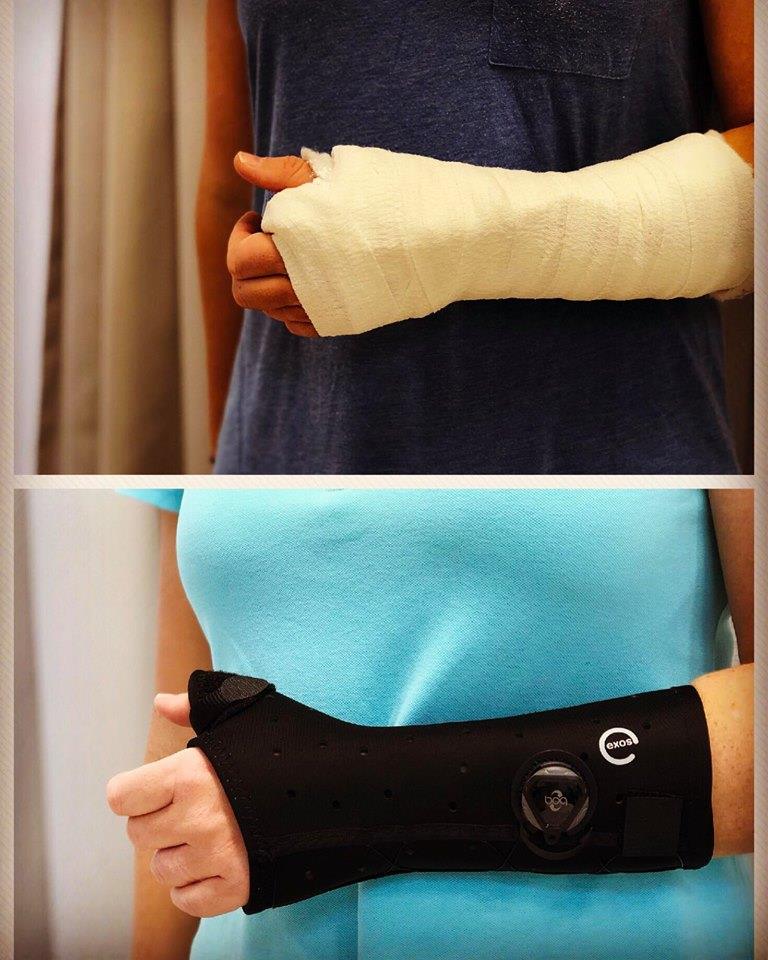
The key to getting a good result after a distal radius fracture (or any other fracture) and returning to full function is early management. Activate Physiotherapy offer same day appointments to attend their fracture clinic to ensure your distal radius fracture is managed with the best management from the start.
Following your Xray our Physiotherapists will fit you into a custom short arm fracture splint. In most straight forward cases your distal radius fracture will be immobilised for around 6 weeks. Our approach is unique and our physiotherapists understand the importance of integrating your rehab during the healing process and will assist you with a rehabilitation program at the various stages of your healing journey. This reduces the complications that often occur from wrist fractures.
How to Make a Fracture Clinic Appointment
Making an appointment at our fracture clinic is as easy as booking online for your nearest Brisbane based Activate Physiotherapy clinic in Stafford or Gumdale.
No Xray? No problem!
We can arrange bulk-billed xrays to confirm diagnosis and monitor healing.
Need your cast removed?
We can help with that too! We are able to remove backslabs and full plaster or polyester casts